
- Hyderabad, India
- +91-9121142043
- dr.meher83@gmail.com
- Book An Appointment

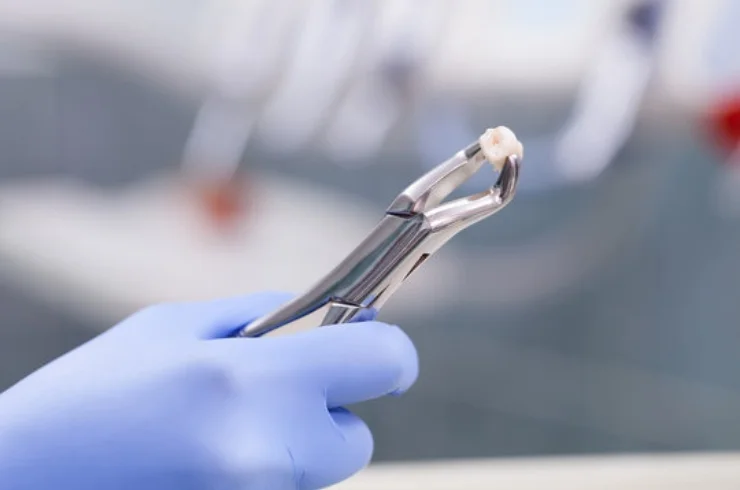
Wisdom tooth extraction is a common dental procedure to remove one or more of the third molars, typically due to complications or impaction.
Wisdom tooth extraction is typically a safe procedure with proper care leading to smooth recovery.
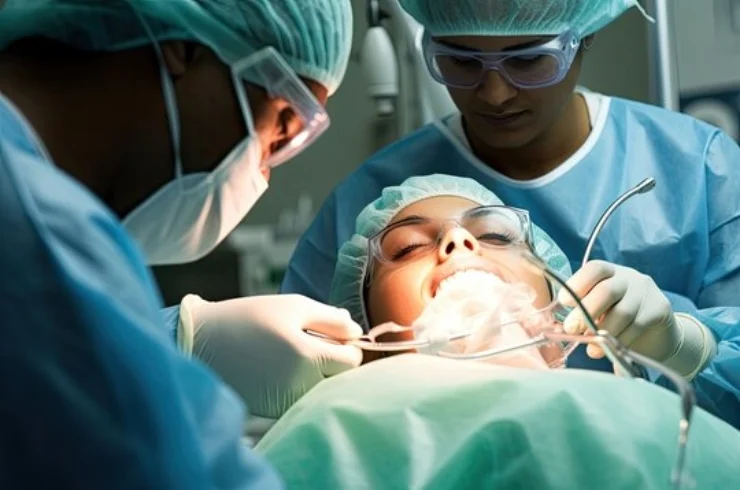
Jaw surgeries refer to various procedures aimed at correcting structural issues in the jaw, improving function, or enhancing aesthetic appearance. Commonly performed by oral and maxillofacial surgeons, these surgeries may involve the upper jaw (maxilla), lower jaw (mandible), or both.
Jaw surgeries can significantly enhance quality of life by correcting functional and aesthetic issues. It’s essential to consult with a qualified oral and maxillofacial surgeon for personalized advice and treatment options.
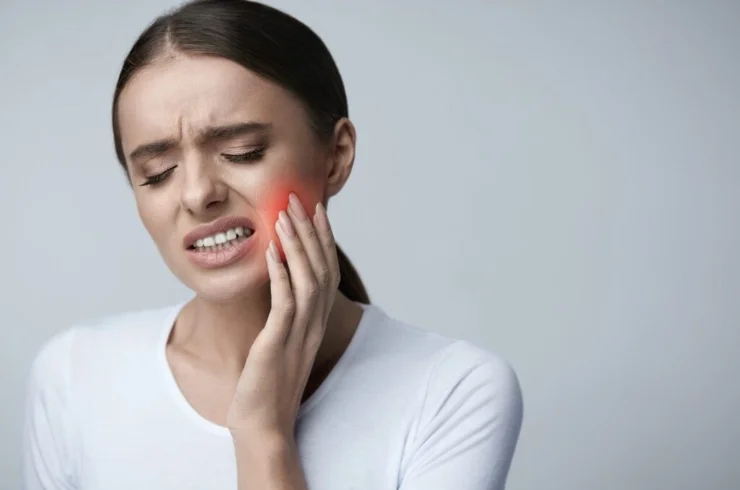

Temporomandibular joint (TMJ) disorder refers to a set of conditions affecting the jaw joint and surrounding muscles, leading to pain, discomfort, and difficulties in jaw movement.
A healthcare professional will typically conduct a thorough examination, which may include:
TMJ disorder can often be managed through a combination of conservative and invasive treatments tailored to the individual’s needs. Consulting with a healthcare professional is essential for a proper diagnosis and personalized treatment plan.
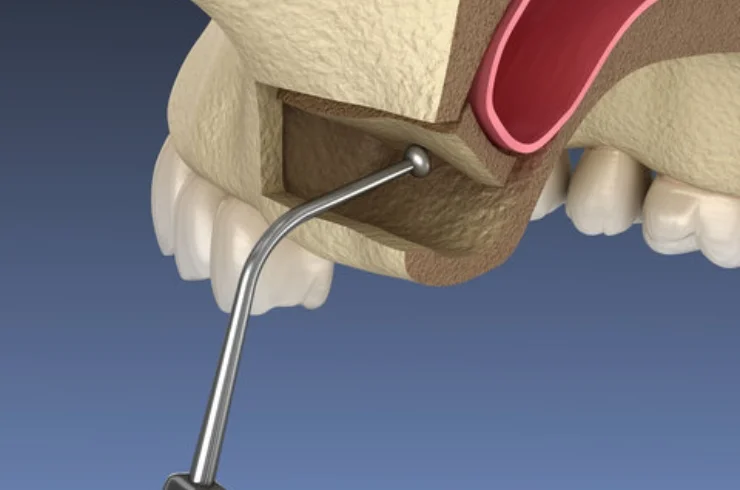
Bone grafting is a surgical procedure used to replace or augment missing bone in the jaw. It is often performed to improve the success rate of dental implants, especially in cases of bone loss due to periodontal disease, trauma, or congenital conditions.
Sinus lifting, or sinus augmentation, is a specific type of bone grafting procedure aimed at increasing the bone height in the upper jaw by lifting the sinus membrane and placing bone graft material in the sinus area. This procedure is often necessary before placing dental implants in the back of the upper jaw.
Bone grafting and sinus lifting are essential procedures in modern dentistry, particularly in the context of dental implants. They enable successful rehabilitation of individuals with bone loss, enhancing both function and aesthetics. A thorough consultation with a dental professional is crucial for personalized treatment planning.